Interactive Heart Diagram
Learn the anatomy of the heart with our interactive diagram! Click on the part to listen to its pronunciation and improve your medical knowledge.
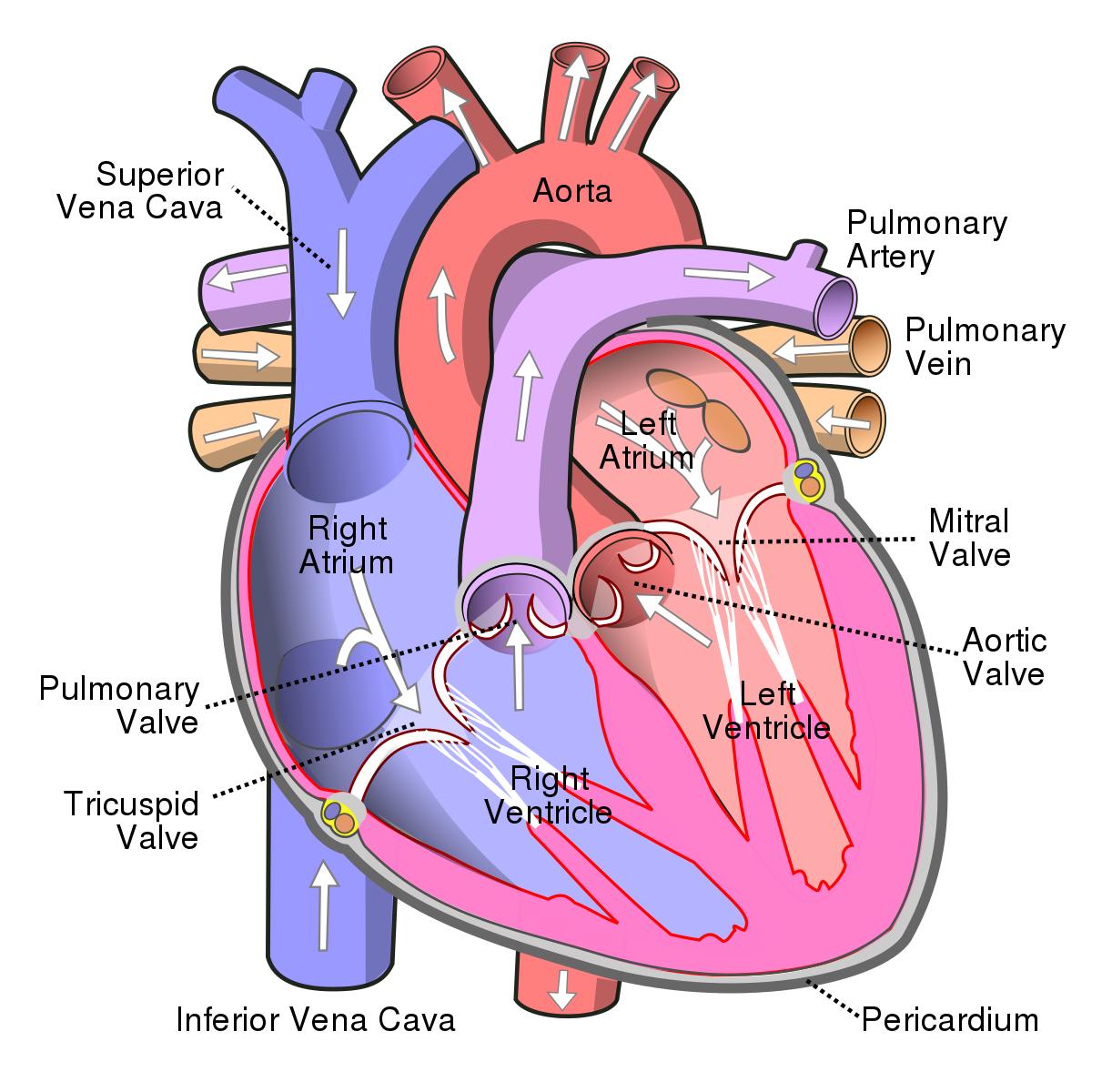
a large vein that carries de-oxygenated blood from the upper body back to the heart's right atrium
a large vein that carries de-oxygenated blood from the lower body back to the heart's right atrium
receives de-oxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava and pumps it to the right ventricle
receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary vein and pumps it to the left ventricle
a valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle that prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium
receives de-oxygenated blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs through the pulmonary artery
receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps it to the rest of the body through the aorta
a valve located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery that prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle
carries de-oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide
The pulmonary veins are four blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
a valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle that prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium
a valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta that prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle
The aorta is the largest artery in the body that carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body. It branches off into smaller arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the organs and tissues.
a double-layered sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels
